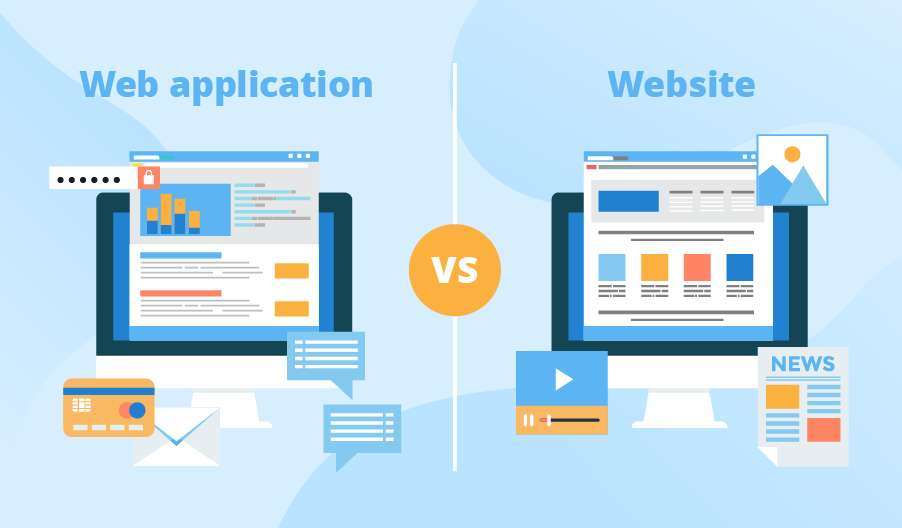
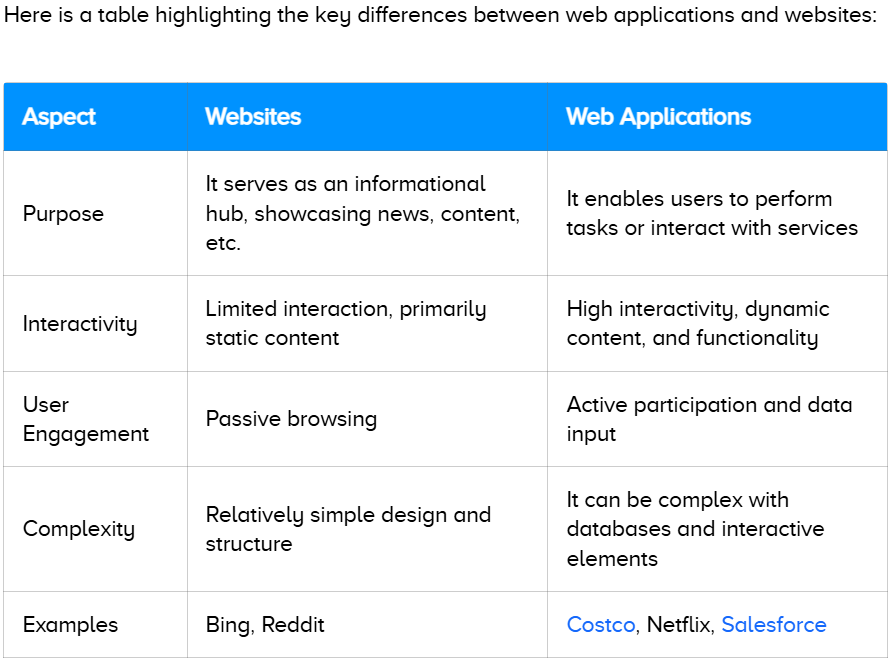
The main distinction between web apps and websites lies in their functionality and interactivity. Websites primarily act as information hubs, designed for content delivery. They offer navigable visual and textual content that users can view but not manipulate. Accessible through a browser, websites are compatible with a wide range of devices.
In contrast, web applications offer interactive functionality, allowing users to complete tasks, conduct transactions, or utilize services directly within the browser. Unlike traditional websites, web apps enable users not only to access content but also to manipulate and modify data.
Websites are basic and provide limited features, whereas a robust web application delivers extensive functionality. For example, an eCommerce website may let users browse products and make purchases, but a web app enhances the experience with features like order tracking, customer support, and personalized recommendations.
Users don’t need to download or install websites. However, registration is often required to access extra features unavailable to unregistered visitors. For example, on a news website, anyone can browse articles without signing up, but commenting on posts requires logging in. This verification process helps confirm user identity and prevents spam.
Web applications are highly customizable and offer numerous features, but they require authentication to maintain user security. For example, when signing up for a social networking web app like Facebook, users receive a unique identification number to create their account. The system alerts users if their login credentials are weak, as unchanged weak passwords may allow hackers to gain access and steal information. Thus, authentication is essential for logging into web applications.
Examples of well-known websites include Wikipedia.com and Google.com. A notable example of a web application is an online banking platform, which enables users to conduct transactions and carry out various other financial activities.